

Electrical stimulation plays a significant role in the medical field as a treatment for muscle weakness, with a wide range of applications. Below, we introduce its main uses.
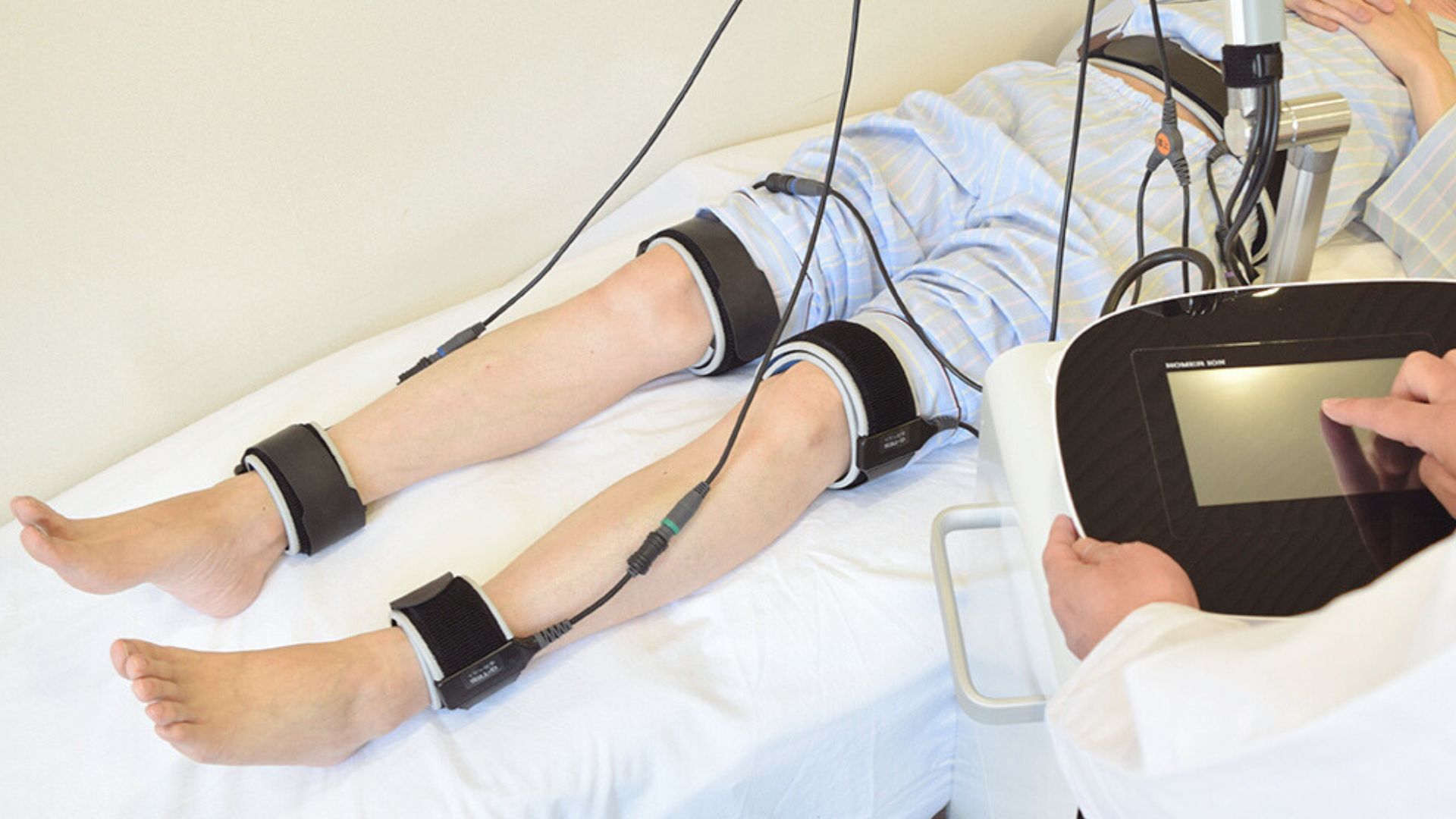
Pain is one of the most common reasons for visiting a medical facility and represents a serious issue for many patients. Electrical stimulation is one of the effective treatment methods for pain.In particular, Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) delivers low-frequency electrical stimulation to nerves through the skin, altering pain perception and helping to relieve discomfort.As a non-pharmacological therapy for pain management, it also offers patients an alternative treatment option.
Electrical stimulation is also effective in maintaining muscle strength and promoting the recovery of muscle function.After surgery or injury, patients need to prevent muscle atrophy and restore function. In such cases, electrical stimulation activates the muscles and helps alleviate pain.This process plays a crucial role in rehabilitation and supports patient recovery.Today, electrical stimulation is also recognized as an important method for preventing and maintaining muscle strength in elderly individuals.
Neuropathy symptoms can cause significant distress to patients. Electrical stimulation is extremely useful in the treatment of neuropathy.In particular, nerve stimulation therapy is applied to patients with diabetic neuropathy and neuralgia.Electrical stimulation helps adjust neural circuits and can alleviate sensory abnormalities and pain. It plays a crucial role in improving the patient’s quality of life.
Note: Neuropathy refers to the condition where small blood vessels become blocked by blood clots, preventing blood flow to the affected nerves, leading to localized damage.
Fractures can significantly disrupt a patient’s daily life, and recovery may take time. This is where electrical stimulation comes into play.Electrical stimulation promotes bone healing by delivering low-frequency electrical currents to the fracture site. This process is referred to as “fracture healing enhancement.”
Through electrical stimulation, the growth of new bone tissue is stimulated, and the fracture site is strengthened. As a result, recovery from the fracture is accelerated, and the patient’s quality of life is improved.Electrical stimulation is especially useful for treating fractures that are difficult to heal or for elderly patients, making it a valuable option.
Brain stimulation therapy* has brought groundbreaking advances in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.Various techniques, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), are being used.These therapies involve electrical stimulation to target specific areas of the brain and adjust neural circuits.For example, DBS is used for patients with Parkinson’s disease and depression, with the expectation of symptom improvement.Electrical stimulation therapy provides a valuable treatment option for patients who do not respond to medication or surgery.
*Brain stimulation therapy refers to a treatment method where thin electrodes are inserted into specific areas of the brain to deliver electrical stimulation.
Electrical stimulation is also effective in managing the symptoms of inflammatory diseases*.Particularly for patients suffering from conditions such as arthritis and tendinitis, Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is used.TENS devices deliver low-frequency electrical stimulation to the nerves through the skin, reducing pain and inflammation.This helps patients alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with inflammatory diseases, improving their quality of life in daily activities.
*Inflammatory diseases refer to a group of conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and atopic dermatitis, that cause inflammation in tissues due to immune response dysfunction.
In addition to the conditions mentioned above, there are researchers investigating the effects of electrical stimulation on maintaining bodily functions,such as its impact on “glucose metabolism” and its potential as an “alternative method for dementia prevention.”
The results of future studies are highly anticipated.

